Hair loss in bodybuilding: what causes it & how to fix it
Hair loss, or androgenic alopecia, is a sensitive and often emotional concern among male bodybuilders—particularly those who use anabolic steroids or other hormonal enhancements.
While most athletes begin enhancement protocols to improve their physique, strength, or competitive edge, some are blindsided by the unintended consequence of hair thinning or balding. In a culture where aesthetics matter, this can be particularly distressing.
Understanding how and why hair loss occurs in enhanced bodybuilders, as well as what steps can be taken to prevent it, is crucial for anyone considering or currently running performance-enhancing compounds.
What Causes Hair Loss in Bodybuilders?
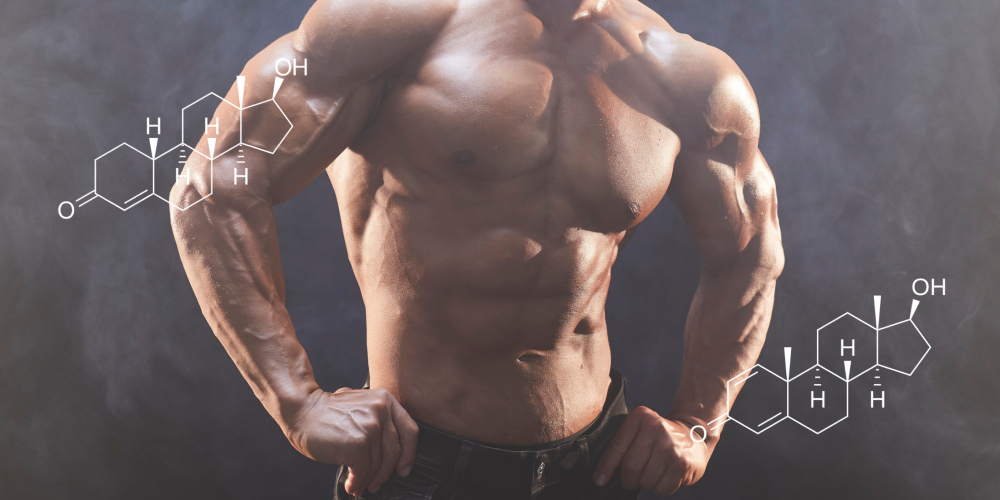
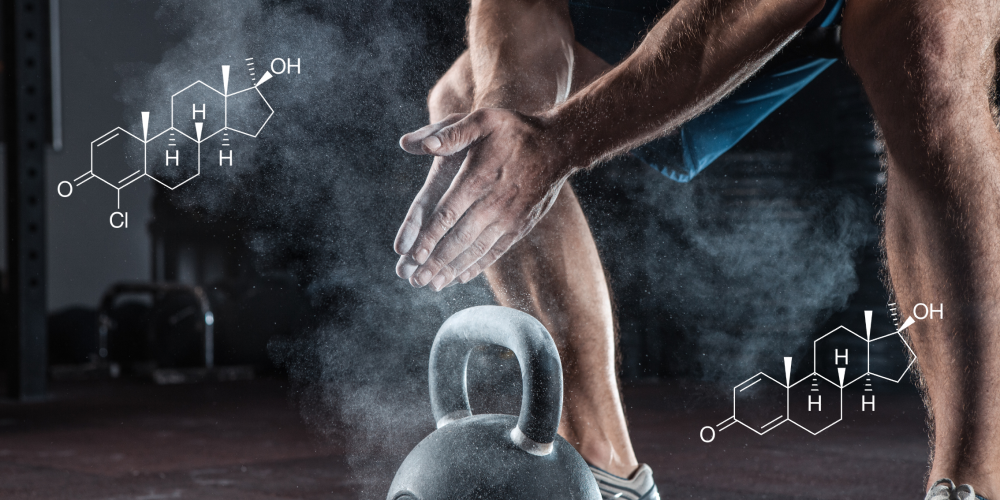
Hair loss in bodybuilding is primarily androgen-driven. The most common form, androgenic alopecia, is caused by the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent androgen. DHT binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles—particularly those located on the scalp—and gradually shrinks them, shortening the hair’s growth phase (anagen phase) and causing the hair to thin and fall out over time.
Several anabolic steroids—especially Testosterone, Trenbolone and DHT-derivatives like Masteron, Winstrol, Proviron, and Anavar—either directly introduce more DHT into the system or increase the body’s DHT load by upregulating 5-alpha-reductase enzyme activity.
For genetically susceptible individuals, even moderate steroid use can initiate or accelerate male pattern baldness.
It’s important to understand that hair loss due to DHT is not a side effect that affects everyone equally. Some individuals with strong genetic resistance to DHT-related follicular damage may run heavy cycles for years without hair loss. Others may notice hairline recession within weeks of starting a mild cycle. This variability makes hair loss one of the most unpredictable and frustrating side effects.
Common Risk Factors
Several factors can increase your risk of experiencing hair loss during or after a cycle:
Genetic Predisposition
If your father, grandfather, or uncles have male pattern baldness, you’re statistically more likely to experience it too.
Type of Compound Used
DHT-based steroids (e.g., Winstrol, Masteron, Anavar) are the most aggressive on scalp hair.
Dosage and Duration
Higher doses and longer cycles create more prolonged exposure to DHT and increase follicular stress.
Lack of DHT Management
Not using DHT blockers or inhibitors can leave hair follicles vulnerable to damage.
Stress and Recovery
Chronic stress, poor sleep, and inflammation can exacerbate hair shedding by disrupting the hair growth cycle.
Post-Cycle Hormonal Crash
A sudden drop in testosterone after a cycle (without proper PCT) can shift the hormonal environment and worsen shedding.
Prevention and Treatment Strategies
Mitigating hair loss requires a multi-pronged approach, particularly for those who are genetically predisposed. The earlier action is taken, the more effective the results tend to be.
Finasteride (Propecia)
A pharmaceutical 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor that reduces the conversion of testosterone to DHT by up to 70%. It’s effective for many, but side effects such as decreased libido, mood swings, and erectile dysfunction have been reported in a subset of users.
Dutasteride
A stronger 5AR inhibitor that blocks both type I and type II isoenzymes. It reduces DHT even more aggressively than finasteride, but it may come with a higher side effect burden.
RU58841
A research chemical applied topically to the scalp that binds to androgen receptors in hair follicles, preventing DHT from exerting its miniaturizing effects. Because it doesn’t affect systemic DHT levels, it tends to avoid sexual side effects.
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
A vasodilator that increases blood flow to the scalp and stimulates hair growth. It doesn’t block DHT, so it works best in combination with a DHT inhibitor.
Ketoconazole Shampoo (Nizoral)
Has anti-androgenic and anti-inflammatory effects. Using it 2–3 times a week can help maintain scalp health and reduce DHT at the follicle level.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) or Red-Light Therapy
Devices like laser caps or combs may promote mitochondrial activity in follicles, potentially extending the growth phase.
Nutritional Support
Zinc, biotin, vitamin D, omega-3s, and collagen all support hair health and may help prevent unnecessary shedding due to deficiencies.
Hair loss doesn’t have to be an inevitable side effect of bodybuilding—especially not in the enhanced realm. While DHT-driven androgenic alopecia is largely genetic, understanding which compounds are most likely to accelerate the process and how to intervene early can preserve both hair and confidence. Modern therapies offer a wide range of both pharmaceutical and over-the-counter options to mitigate the risks. With a little planning, it’s entirely possible to achieve elite muscularity without sacrificing your hairline in the process.