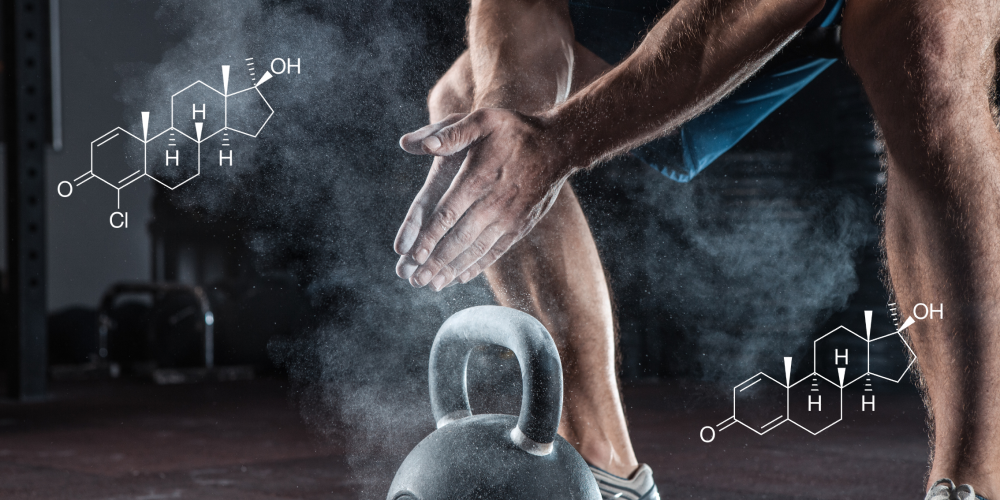
Cardarine – exercise in a pill
Cardarine, also known as GW-501516, is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR-δ) agonist initially developed to treat metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Over time, it gained immense popularity in the fitness and bodybuilding communities for its ability to enhance endurance, improve fat metabolism, and aid in achieving a lean, defined physique.
Mechanism of action: PPAR-δ Activation
Cardarine works by activating the PPAR-δ receptor, which plays a key role in energy metabolism. This activation shifts the body’s energy source from carbohydrates to stored fats, effectively increasing fatty acid oxidation and improving overall metabolic efficiency.
Unlike stimulants or other fat burners, Cardarine does not directly interact with the central nervous system. Instead, it boosts endurance and fat loss without causing jitters, crashes, or increased heart rate.
Benefits of Cardarine
Enhanced endurance
Cardarine is renowned for its ability to significantly improve stamina and physical endurance. Users often report being able to train longer and harder, whether during cardio sessions or high-intensity weightlifting. This makes it a favorite among endurance athletes, such as runners and cyclists.
Accelerated fat loss
By increasing fatty acid oxidation and improving metabolic efficiency, Cardarine promotes steady fat loss. Users frequently experience reductions in body fat while preserving lean muscle, making it ideal for cutting phases or body recomposition goals.
Improved recovery
Cardarine’s ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress accelerates recovery times between workouts. This allows users to maintain a high training frequency without risking overtraining or prolonged muscle soreness.
Heart health benefits
Research shows that Cardarine can improve cholesterol profiles by increasing HDL (good cholesterol) and reducing LDL (bad cholesterol). These cardiovascular benefits make it a potentially useful tool for individuals concerned about heart health.
Blood sugar regulation
Cardarine helps stabilize blood sugar levels and increase insulin sensitivity. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with impaired glucose metabolism or those seeking to avoid fat gain during high-calorie phases.
Potential Side Effects
Cardarine is generally well-tolerated when used responsibly, but some potential concerns exist:
Cancer risk in animal studies
Preclinical studies showed an increased risk of cancer in rodents exposed to extremely high doses of Cardarine for prolonged periods. However, these doses far exceed those typically used by humans, and no definitive evidence of similar risks in humans has been reported.
Digestive issues
Some users may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea or upset stomach.
Unknown long-term effects
As with many research chemicals, the long-term safety profile of Cardarine in humans remains unclear, emphasizing the importance of moderation and responsible use.
Recommended Dosage and Cycle Length
Cardarine is typically dosed at 10–20 mg per day, depending on individual goals:
- For Endurance and Performance: 10 mg per day is sufficient to boost stamina and athletic performance.
- For Fat Loss and Body Recomposition: 15–20 mg per day is optimal to maximize fat oxidation and metabolic benefits.
Cardarine has a long half-life (~24 hours), so it only requires once-daily dosing. It can be taken with or without food, based on personal preference.
Typical cycles last 8–12 weeks, followed by a break to ensure long-term safety and avoid potential side effects.
Stacking Cardarine with Other Compounds
Cardarine is often stacked with other performance-enhancing compounds for synergistic effects:
- With Anabolics (AAS & SARMs): Which preserve or build muscle during cutting cycles.
- With Fat Burners: For accelerated fat loss and improved energy expenditure.
Due to its non-suppressive nature, Cardarine does not require post-cycle therapy (PCT) and can complement most cycles seamlessly.
Cardarine (GW-501516) has earned its reputation as a versatile compound for endurance enhancement, fat loss, and metabolic health. Its ability to improve performance without affecting hormonal balance makes it a popular choice for endurance athletes and bodybuilders alike.
References
-
Oliver, W. F., et al. (2001). “Activation of PPAR-δ Promotes Fatty Acid Oxidation and Increases Endurance in Mice.” Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(42), 38870-38876.
-
Risérus, U., et al. (2008). “PPAR-δ activation: effects on metabolism and potential implications in the treatment of metabolic disorders.” Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1771(8), 1264-1271.
-
Margolin, N., et al. (2011). “Effects of PPAR-δ Agonists on Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in Humans.” Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology, 38(5), 376-382.